03 Anti-inflammatory effect of ADSC
페이지 정보

본문
1. what is inflammation?
Inflammation is part of the body's complex response to harmful stimuli such as pathogens, damaged cells, and irritants. Many people mistakenly believe that inflammation is a disease, but inflammation is a necessary response to protect the body. However, excessive inflammatory response can actually cause damage to the body.
Inflammation has five characteristics: Heat, Pain, Redness, Swelling, and Immobility. Among these, heat and redness are caused by increased blood flow to the inflamed area, edema is caused by more plasma components leaking from the blood to the inflamed area, and pain is caused by histamine and bradykinin generated during the inflammatory reaction stimulating the nerve endings. It happens because you do it. These factors combine to cause loss of function in specific areas.
2. How does inflammation occur?
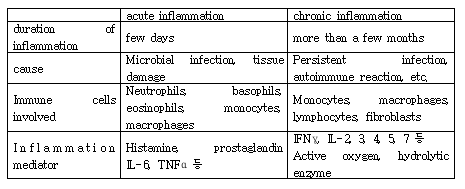
Before mentioning the mechanism of inflammation, let me tell you about the types of inflammation. Inflammation is broadly classified into acute inflammation and chronic inflammation. Acute inflammation and chronic inflammation are classified by the duration of inflammation. Acute inflammation lasts for a short period of time and disappears, while chronic inflammation lasts for a long period of time.
Acute inflammation is caused by microbial infection or tissue damage. Inflammation is caused primarily by the influx of neutrophils into the infected or damaged area. On the other hand, chronic inflammation is caused by persistent infection or autoimmune disease. Inflammation continues as various immune cells gradually flow into the area of infection or disease. White blood cells that flow into the inflamed area secrete inflammatory mediators such as histamine, IFNγ, and interleukin, causing inflammatory symptoms.
3. How do ADSCs exert anti-inflammatory effects?
If you watch the video about the effect of ADSCs on immunity, you can see that ADSCs are involved in the differentiation of macrophages and play a role in regulating the activity of T cells or directly regulating the activity of B cells. These ADSC actions also contribute to the anti-inflammatory effect.
In addition to these mechanisms, local regulators secreted by ADSCs can exert anti-inflammatory effects by controlling the activity of monocytes (Guillén et al., Frontiers in Physiology, Volume 9, Article 661). Guillén et al. added ADSC culture medium (CM) to monocyte culture medium and confirmed the level of inflammatory mediators secreted by monocytes. As shown in the graph below, when only ADSC culture medium (CM) is treated, the secretion of inflammatory mediators TNFα and prostaglandin increases compared to the untreated control group, but ADSC culture medium (CM) is applied to cells treated with LPS, an inflammatory substance.
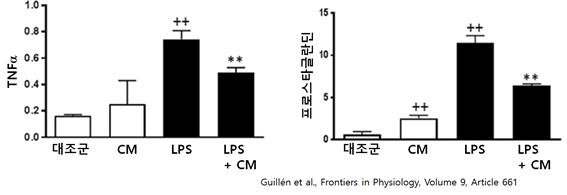
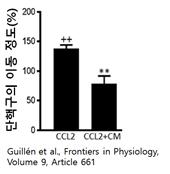
It can be seen that the treatment actually reduces the secretion of TNFα and prostaglandin. These results clearly demonstrate that local regulators secreted from ADSCs can control the inflammatory response by monocytes. The inflammatory response attracts monocytes to the site of inflammation, and at this time, a cytokine called CCL-2 triggers the movement of monocytes. To determine whether ADSC culture medium (CM) affects the migration of monocytes, we treated the migration of monocytes with CCL-2 and CM together. As a result, CM reduced the migration of monocytes, as shown in the graph below.
In other words, ADSC can exert an anti-inflammatory effect by preventing monocytes from being attracted to the site of inflammation and preventing inflammation from growing.
In addition to these results, Guillén et al. also showed through various experiments that CM inhibits the macrophage activity of monocytes. These series of results clearly demonstrate that ADSCs can exert an anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing the immune response caused by monocytes through the local regulators they secrete.
4. What diseases will the anti-inflammatory effect of ADSC help treat?
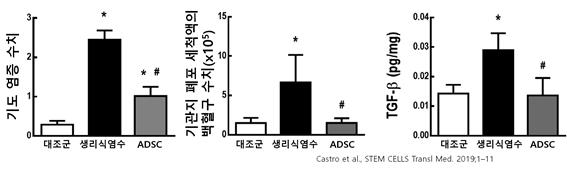
It is expected to be helpful in treating diseases caused by excessive inflammatory reactions, such as autoimmune diseases. In fact, studies have shown that injecting ADSCs more than three times alleviates inflammation in dust mite-induced asthma and reduces lung remodeling (Castro et al., STEM CELLS Transl Med. 2019;1–11 ).
According to a study by Castro et al., the overall inflammation level was lowered in asthmatic mice injected with ADSC, and in particular, the white blood cell count and the level of the inflammatory substance TGFβ were all reduced to the same level as the normal control group.
In another study, the recovery of arthritis was histologically examined after ADSCs were injected into the joints of mice with rheumatoid arthritis (Ueyama et al., Scientific Reports, 2020. 10:3076).
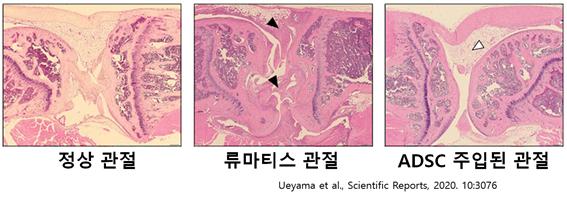
As clearly observed in the above results, it can be seen that in joints where rheumatoid arthritis occurs, cartilage is destroyed and many inflammatory cells have infiltrated. On the other hand, joints treated by injecting ADSCs show a shape that is almost similar to normal joints. The above research results clearly demonstrate that the anti-inflammatory effect of ADSCs can actually treat diseases. If this video helped resolve your questions about the anti-inflammatory effect of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC),
- PrevTreatment of liver disease by ADSC 24.04.16
- NextWhat is aging? 24.04.16
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.





 +82-2-532-2856
+82-2-532-2856 info@panacellbio.com
info@panacellbio.com 521, Teheran-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea
521, Teheran-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea